Ideal Gas Law R Values / Ideal gas law practice mccpot / Calculations using the ideal gas equation are included in my calculations book (see the link at the very bottom of the page), and i can't repeat them here.
Ideal Gas Law R Values / Ideal gas law practice mccpot / Calculations using the ideal gas equation are included in my calculations book (see the link at the very bottom of the page), and i can't repeat them here.. The sheer amount of information can be confusing, and it is wise to develop a systematic method to solve them: Due to this fact the ideal gas law will only give an approximate value for real gases under normal condition that are not currently approaching qualification. 1) jot down the values of p , v , n , and t. Substitute the values in the below temperature equation: Further parameters that enter the equation are the volume v of the container holding the gas and the amount n (in moles) of gas contained in there.
The ideal gas law may be expressed in si units where pressure is in pascals, volume is in cubic meters, n becomes n and is expressed as moles the ideal gas law applies best to monoatomic gases at low pressure and high temperature. The kinetic theory of gases. Say out loud liter atmospheres per mole kelvin. this is not the only value of r that can exist. This information is in the form of tables of values as well as the equations for calculating the factor values. .gas law, r is the ideal gas universal constant and has a value of 8.314 4621 joules/(mol k).

The ideal gas law can be viewed as arising from the kinetic pressure of gas molecules colliding with the walls of a container in accordance with newton's laws.
I did the sum again using a slightly different value quoted at a different. 1) jot down the values of p , v , n , and t. The ideal gas law allows for us to determine what will happen to a contained system with an ideal gas inside, based on these different variables. The kinetic theory of gases. Say out loud liter atmospheres per mole kelvin. this is not the only value of r that can exist. While this law specifically applies to ideal gases, most gases approximate the ideal gas law under most conditions. Apply the ideal gas law to solve problems in chemistry. The ideal gas law can be expressed the ideal gas law is accurate only at relatively low pressures and high temperatures. Notice the weird unit on r: The approximate value is generally accurate under many conditions. Ideal gas law formula derivation in physics or chemistry, universal constant r, ideal gas molecules, mixed pressure of perfect gases, equation of state. Ideal gas law equation calculator solving for pressure given moles, universal gas constant, temperature and volume. The ideal gas law is the equation of state of an ideal gas (also known as a perfect gas) that relates its absolute pressure p to its absolute temperature t.
The classical carnot heat engine. Ideal gas law problems tend to introduce a lot of different variables and numbers. .gas law, r is the ideal gas universal constant and has a value of 8.314 4621 joules/(mol k). This constant quantifies the relationship between the here, the value of r depends on gas and is different for each gas as all gases will have same ru but different m. The kinetic theory of gases.
The value of r depends on the units used.
Ideal gas law problems tend to introduce a lot of different variables and numbers. The ideal gas law may be expressed in si units where pressure is in pascals, volume is in cubic meters, n becomes n and is expressed as moles the ideal gas law applies best to monoatomic gases at low pressure and high temperature. The sheer amount of information can be confusing, and it is wise to develop a systematic method to solve them: Universal constant values unit and dimension can be calculated from ideal gas law, pv = nrt. The approximate value is generally accurate under many conditions. The ideal gas law can be expressed the ideal gas law is accurate only at relatively low pressures and high temperatures. The molar gas constant (also known as the gas constant, universal gas constant, or ideal gas constant) is denoted by the symbol r or r. The ideal gas law is the equation of state for a hypothetical gas. This ideal gas law calculator is also known as a gas pressure calculator, a molar volume calculator or a gas volume calculator because you can use it to find different values. The classical carnot heat engine. The ideal gas law is a simple model that allows us to predict the behavior of gases in the world. Ideal gas law calculations pv=nrt tutorial with worked examples for chemistry students. The units of the universal gas constant r is derived from equation pv = nrt.
While this law specifically applies to ideal gases, most gases approximate the ideal gas law under most conditions. .gas law, r is the ideal gas universal constant and has a value of 8.314 4621 joules/(mol k). Its value depends on the units used. A gas whose particles exhibit no attractive interactions whatsoever; To account for deviation from the ideal situation an other factor.
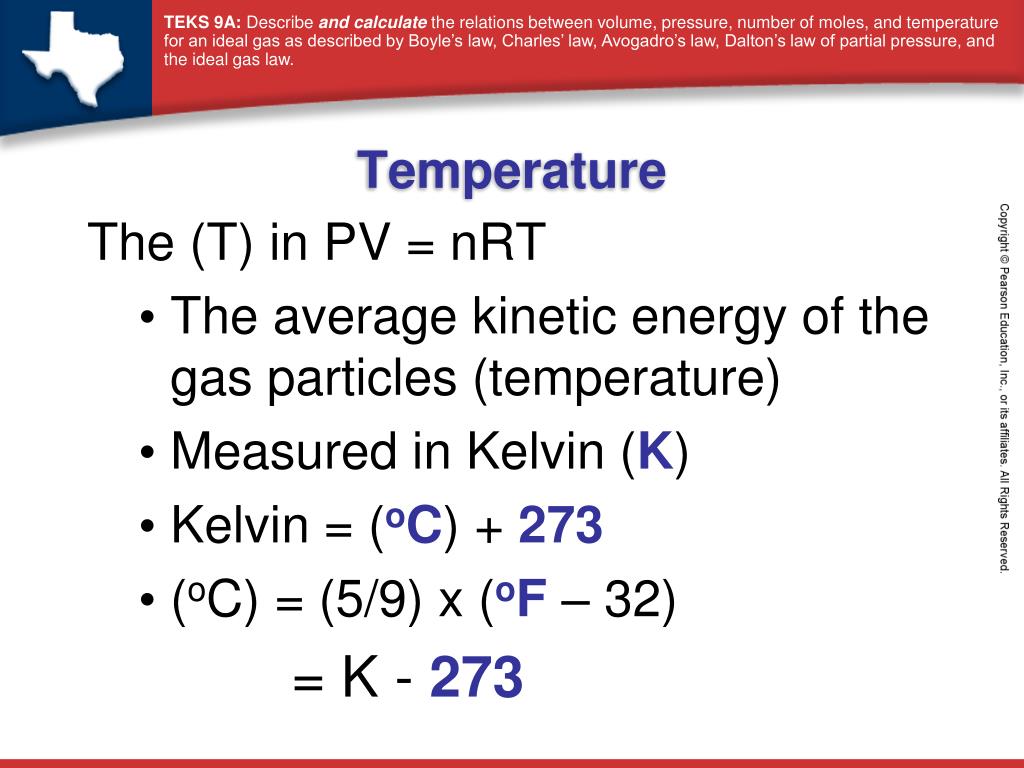
The temperature is taken to be.
This ideal gas law calculator is also known as a gas pressure calculator, a molar volume calculator or a gas volume calculator because you can use it to find different values. The ideal gas law is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. But there is also a statistical element in the determination of the average kinetic energy of those molecules. .gas law, r is the ideal gas universal constant and has a value of 8.314 4621 joules/(mol k). It's very simple, easy to use, and easy to understand. It is the molar equivalent to the boltzmann constant, expressed in units of energy per temperature increment per mole, i.e. Enter the values, leaving blank the variable you wish to solve for Select the variable to solve for: One mole of any gas at standard temperature and pressure (stp) occupies a standard volume of 22.4 liters. To account for deviation from the ideal situation an other factor. Here are the steps to follow when using this online tool Ideal gas law formula derivation in physics or chemistry, universal constant r, ideal gas molecules, mixed pressure of perfect gases, equation of state. The ideal gas law can be viewed as arising from the kinetic pressure of gas molecules colliding with the walls of a container in accordance with newton's laws.
Komentar
Posting Komentar